WAYS TO BUILD BRAND LOYALTY AND LOYAL CUSTOMERS
We have compiled the steps of creating brand loyalty and loyal customers for you.
The term brand loyalty continues to be one of the effective variables in marketing by constantly renewing it. In short, brand loyalty can be defined as the strength of the consumer's belief in the brand. Rational and emotional information about the brand plays a fundamental role in shaping consumers' preferences between products/brands. Consumers' perception of determinative features in a brand and their being affected by these features can increase the loyalty (loyalty) to that brand.
It is seen that there are three different approaches in the literature, these are behavioral, attitudinal approaches to brand loyalty, and attitudinal and behavioral approaches consisting of a combination of these two. According to the behavioral approach, brand loyalty is directly proportional to the repeat purchase, the person shows his loyalty as long as he buys the brand and the loyalty measurement can be made accordingly. In other words, in studies conducted according to this approach, loyalty is only considered as a repeat purchase behavior. However, according to this approach, repeated purchases that consumers show out of loyalty also constitute brand loyalty.

However, not every brand that is purchased continuously has been able to achieve loyalty. For example, the consumer who constantly buys souvenirs or other products at 1 million shops is not loyal to this brand; fluctuations may occur with price indexed changes, and the consumer may turn to brand change in possible situations. Therefore, attitudinal behavior criticizes the fact that the event is limited to re-purchase and also deals with the emotional and psychological dimensions of the event.
According to Jacoby Sheth & Kyner , some customers may buy a brand because it is the cheapest in that product line or because its location in the store is convenient. These customers should be differentiated from those who really prefer that brand over the others and buy in line with this preference. He criticized the definition of loyalty as repetitive buying behavior, stating that it is possible for an individual to develop loyalty to goods or services that he has never purchased, and that different customer profiles and different product groups may have different loyalty situations. According to the second approach developed in line with these criticisms, brand loyalty has begun to be seen as a concept that needs to be examined with both behavioral and attitudinal dimensions.
Physical and Emotional (psychological) Dimension of the Brand
There are two dimensions of the brand that make up the personality of the product. The first is the physical brand that is easily understood by everyone; brand name, logo, symbols, packaging, advertisement, slogan, music etc. The essence of the brand, which is the invisible part, creates its psychological dimension. This value, which constitutes the spirit of the brand, is the emotional brand. The emotional brand is the personality that distinguishes the brand from other products and affects the buyer emotionally. It is the most important factor that keeps your brand in the foreground. The most basic factor in creating an emotional bond with your customer is to establish healthy communication .
Even if this does not consume your product, it can create a tight bond between users and your brand. Renvoise, Linstrom and Kotler, who are brand veterans, state that the most effective factor in creating brand loyalty is to appeal to the emotional brain of consumers. For this, you need to create an archetype for the product you offer. '…. If you use the product, you will look like …..” or the X brand will make you look different from the others. In short, in order to appeal to the emotional brain, you need to analyze the characteristics of your target audience well.
AAKER'S LOYALTY PYRAMID
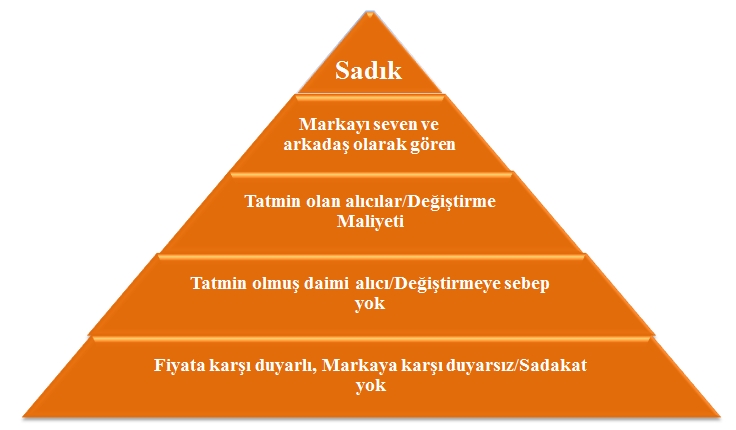
As can be seen, at the bottom of the brand loyalty pyramid, it is price sensitive; There are buyers who are indifferent to brands, where the brand name is of little importance in the purchasing decision, who perceive all brands as similar and who are not loyal to the brand. In the second place are the buyers who are satisfied or at least not dissatisfied with the product features. There is no reason to change the brand for this group of buyers, whose buying behavior has become a habit because they are satisfied with the brand.
In the third row of the loyalty pyramid, there is the group of buyers who are satisfied with the brand and in addition to the costs of changing the brand, such as time costs, monetary costs and performance risk. In the fourth row of the pyramid, there is the group of buyers who are emotionally attached to the brand, who love the brand and see it as a friend. At the top of the pyramid, there are buyers affiliated with the brand. For this group, which is proud to use the brand, the brand is very important for customers to express themselves emotionally.
The brand will be able to create the target audience that it can address by determining the types of loyal customers . It selects the target audience according to the types of customers, whose loyalty is created in the customers with which characteristics, and organizes the brand according to them and makes the sale. As a matter of fact, the target for brands is not just to sell, because brands that only target sales cannot maintain their long-term fate in a highly competitive market. If it does not make some attacks after the sales peak, it will go downhill. This is where building brand loyalty will have to come into play. This can only be achieved by determining customer demands and measuring the demographic characteristics of the audience. The brand will be able to start building loyalty in line with this information it has.
THE STAGE OF BUILDING BRAND LOYALTY WITH THE ACSI MODEL

The main purpose of customer relationship management and customer satisfaction measurement systems is to determine customer loyalty, to increase the number of loyal customers and the loyalty of existing customers. The first academic study on customer loyalty was first done on low-priced goods such as toothpaste and detergent. Later on, customer loyalty was applied in different sectors with different aspects.
It is to ensure the objectivity and reliability of the chain of factors affecting customer loyalty in the models. The effects of this are evaluated by measuring customer complaints and customer loyalty. (With negative customers on social media) The purpose of the model is to help brands and consumers make a situation analysis and know their position. Thanks to the customer satisfaction indexes, a dialogue occurs between consumers and producers.
Businesses see the satisfaction level of their customers by looking at the statistical data in the indexes and take steps accordingly, a customer-centered production process begins and production is made in line with customer requests. The difference in satisfaction between corporate and privatized businesses is learned, and accordingly, government businesses have to take steps to satisfy their customers. It affects the intangible value of the business. The business takes over the competition management with the ratio of loyal customers to its competitors. And finally, the value of the consumer is understood.
Although the first systematic customer satisfaction index was available in Sweden, the American index added two important aspects to this parameter, namely the improvement of the measurement of perceived quality and price tolerances. Thus, the index has become more efficient. The most widely accepted index is *Acsi. In this model, customer expectations, perceived quality and perceived value are the leading factors and these factors serve to measure brand loyalty. Customer expectations cover the general expectations of the customer from the company.. This happens in two ways: First, the expectation shown by considering the characteristics of the previous products offered to the market by the firm. The other consists of estimating the quality that suppliers can bring to market in the future. Therefore, customer expectations also have a two-way (forward-backward) structure. Perceived quality is the customer's evaluation of the quality of the product they use.













0 Comments